Equipotential Surfaces
Equipotential Surfaces: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Equipotential Surfaces, Properties of Equipotential Surfaces, Equipotential Surfaces due to a Point Charge, Equipotential Surfaces in a Uniform Electric Field and, Equipotential Surfaces due to a Dipole
Important Questions on Equipotential Surfaces
What is the angle between the electric field and the plane of an equipotential surface?
Some equipotential surfaces, which are normal to - plane are shown in the adjoining figure the direction of the electric field is:
(A) 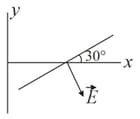
(B) 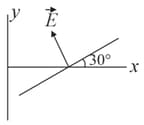
(C) 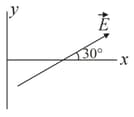
(D) 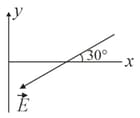
A charge is placed at the centre of a circle of radius . The work done in carrying a charge once round this circle is:
Which of the following option shows the nature of equipotential lines in plane if the electric field intensity at all points in space is given by .
What is the ratio of the electrostatic potential at the corner and the centre point of a charged conducting cube? (The potential is considered at infinity)
The work done in carrying a charge once round a circle of radius with a charge at it's centre is:
The work done to move a unit charge along an equipotential surface from to
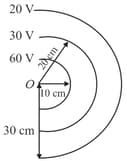
The figure shows equipotential surfaces concentric at 'O'. The magnitude of electric at a distance 'r' meters from 'O' is
A point charge is rotated along a circle around point charge The work done by the electric field on the rotating charge in one complete revolution is
Let the electric field function is . Then the shape of equipotential surface is
The points resembling equal potentials are
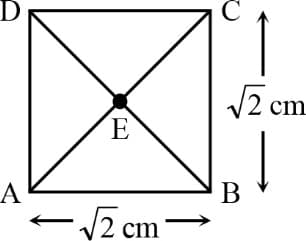
The given square is drawn in a uniform electric field. The potential at the corners , , , and is , , and , respectively. At centre , the potential is , then the magnitude of the electric field is
When two charged conductors are brought into contact, the electric charge on them is shared -
A few spherical equipotential surfaces are shown in the figure. The electric field at any point, at a distance from the centre, is
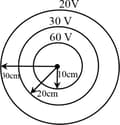
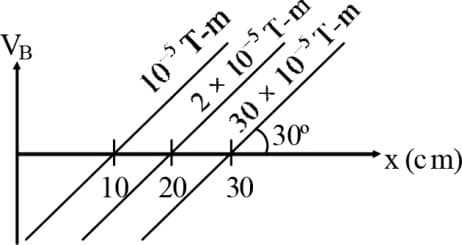
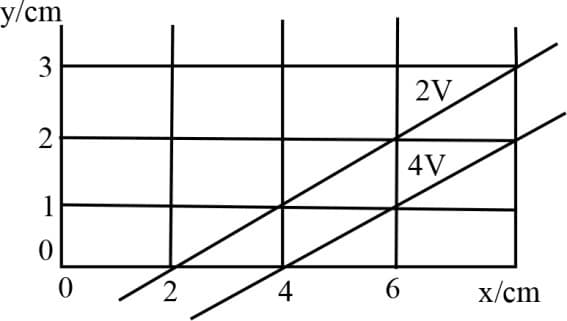
Figure shows two equipotential lines in , plane for an electric field. The scales are marked. The -component and -component of the field in the space between these equipotential lines are respectively
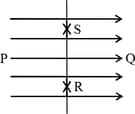
The figure shows three points and in a region of uniform electric field . The line is perpendicular and is parallel to the field lines. Then, which of the following holds good?
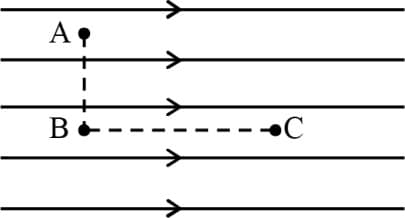
( and represent the electric potentials at the points and , respectively.)
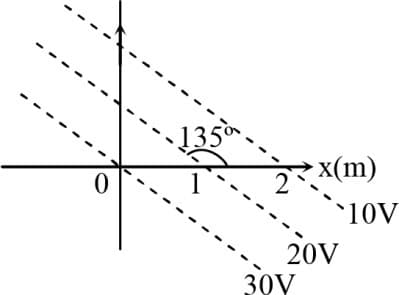
Figure shows a set of equipotential surfaces. The direction of electric field that exists in the region is
At a point in space, the electric field points towards north. In the region surrounding this point, the rate of change of potential will be zero along
Electric lines of force are as shown in the figure. Then the potential at point
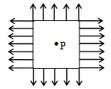
Fig. shows some of the equipotential surfaces of the magnetic scalar potential. The magnetic field at a point in the region is -